Socho tum ek village mein ho. Wahaan ek hi road hai jo har ghar se jodta hai. Sab ek dusre ko chitthi bhejte hai, lekin problem yeh hai ki har bar cycle ya banda leke jana padta hai. Ab socho agar ek aisi system ho jo instantly message pahucha de, bina delay ke… wahi hai “Internet”.
Internet aaj ki duniya ka jadoo hai, par iska jadoo samajhne ke liye pehle samjho ki Network kya hota hai.
Networking Kya Hai?
Networking ka matlab hota hai 2 ya usse zyada devices (jaise computer, mobile) ka ek dusre se judna aur information exchange karna.
- Jaise tumhare ghar ke sab members ek dining table par baith kar baat karte hai — wahi computer ke duniya mein hota hai via cables, routers, switches etc.
- Iska goal hai: Data Sharing, Resource Sharing (jaise printer, internet), Communication (emails, chat).
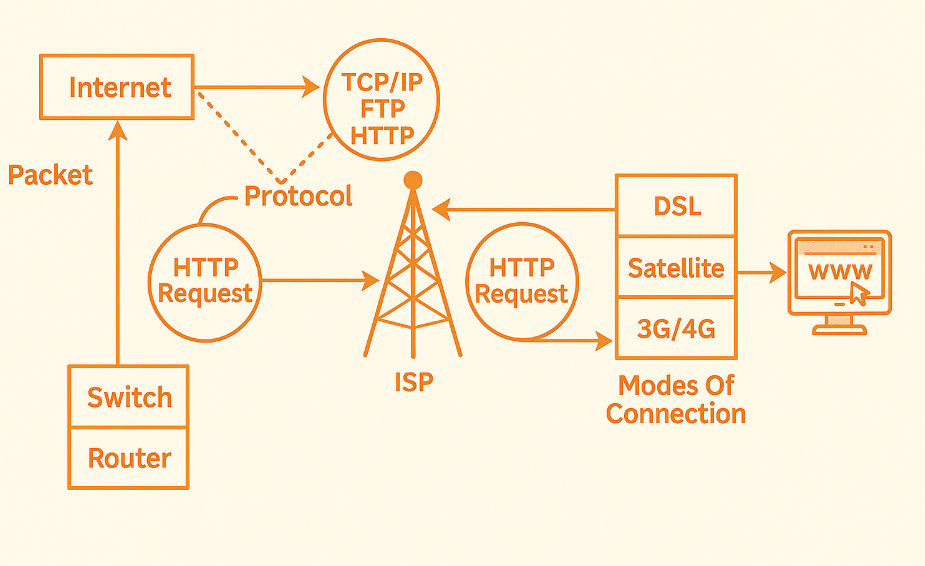
How Internet Works
Socho tum Amazon se ek mobile order karte ho.
- Tumhara phone → Amazon Server ko request bhejta hai
- Woh request travel karti hai tumhare WiFi router se → ISP (Jio, Airtel) → Internet ke kai servers → Amazon ke data center tak
- Amazon ke server se response aata hai wahi raasta wapas
- Tumhare screen pe mobile ka page dikh jata hai.
Yeh pura process sirf 1-2 seconds me hota hai! Isse kehte hai: Client-Server Architecture (detailed explanation neeche milega).
Data Transfer over the Internet
Data kabhi ek baar me transfer nahi hota, balki:
- Sabse pehle data chhote-chhote packets me divide hota hai.
- Har packet ke paas apna source IP aur destination IP hota hai.
- Yeh packets different raasto se jaake wapas jud jaate hai receiver ke device me.
- Agar koi packet lost ho jaye, toh wapas bhejne ka request hota hai.
Example: Ek WhatsApp image bhejne pe woh chhote parts me divide hoti hai → server → receiver tak.
IP Address and Port Number – Kaam Kaise Karte Hai?
IP Address (Internet Protocol Address):
- Har device ka unique ID hota hai – jise hum IP Address kehte hain.
- Jaise ghar ka address hota hai “123, Delhi” waise hi computer ka address hota hai “192.168.1.10”.
Types of IPs:
- IPv4: 32-bit (e.g., 192.168.1.1) — zyada use hota hai.
- IPv6: 128-bit (e.g., 2400:cb00:2048:1::c629:d7a2) — naye system me use ho raha hai because IPv4 addresses khatam ho rahe hai.
Port Number:
- Socho tum ek flat me ho jiska address 22A hai, par tumhe kaunsa kamra chahiye – Bedroom? Kitchen? That’s the port.
- Web (HTTP) = port 80, HTTPS = port 443, Email = port 25, 110 etc.
Types of Networks – LAN, MAN, WAN
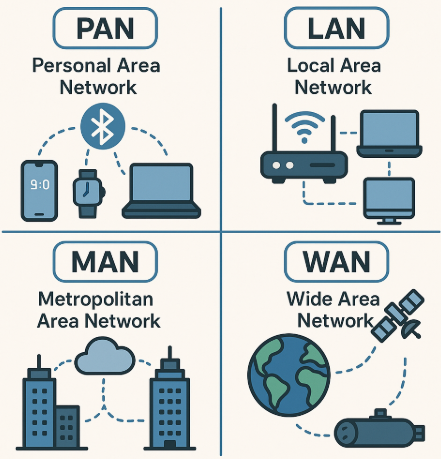
1. LAN – Local Area Network
- Ek chhoti jagah, jaise ghar, office, school.
- Sab devices ek hi building me ho aur ek dusre se connected ho.
Example: Tumhare ghar me sab phone ek WiFi se connected hai — that’s LAN.
2. MAN – Metropolitan Area Network
- Ek shehar ya university campus tak ka area cover karta hai.
- LAN se bada hota hai.
Example: Delhi Metro ka internal data system ya ek university ke sab departments connected ho — that’s MAN.
3. WAN – Wide Area Network
- Bahut bada area cover karta hai — countries, continents.
- Internet = world’s biggest WAN.
Example: Tum Delhi me ho, aur London me kisi ko email bhejte ho. That’s WAN in action.
Network Topologies
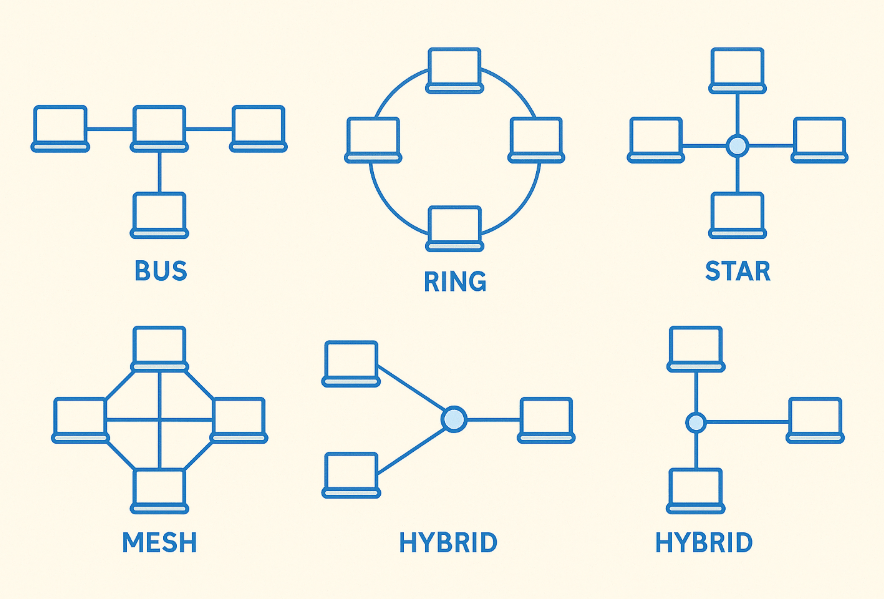
1. Bus Topology:
- Sab device ek single cable se connected hote hain.
- Jaise school me ek bench pe sab bachche baith ke ek line me baat kar rahe ho.
🟢 Pros:
- Simple & Cheap
🔴 Cons:
- Ek wire fail ho gaya = sab system fail
2. Star Topology:
- Sab device ek central device (Switch/Hub) se connected hota hai.
- Jaise ek teacher ke around sab students baith ke question pooch rahe ho.
🟢 Pros:
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Ek wire fail = baaki system safe
🔴 Cons:
- Central device fail = sab band
3. Ring Topology:
- Devices ek circular path me connected hote hai.
- Jaise ek round table conference jaha message left se right pass hota hai.
🟢 Pros:
- Equal access to devices
🔴 Cons:
- Ek node fail = pura ring kaam nahi karega
4. Mesh Topology:
- Har device har dusre se connected hota hai.
- Jaise har banda ek dusre se mobile pe connected ho bina kisi third-party ke.
🟢 Pros:
- Best reliability
- Fault tolerance high
🔴 Cons:
- Bohot zyada wires = Expensive
5. Hybrid Topology:
- Combination of two or more topologies (Star + Ring, etc.)
| Concept | Real Life Example | Key Use |
|---|---|---|
| LAN | Home WiFi | Fast local communication |
| MAN | University Network | Medium-scale data sharing |
| WAN | Internet | Global connectivity |
| IP Address | Home Address | Identify device |
| Port Number | Room Number | Identify service |
Real-Life Use Case:
Socho meri website TechRhym India me hai, aur ek student US se kholta hai. Tab:
- Browser → DNS resolve → Server IP find → Server se page load → User ke browser me dikhega.
Yeh sab Networking ke bina possible hi nahi.
click here for computer networking part 2




2 thoughts on “Networking Part 1: Internet, Data Transfer, IP, Network Types, Topologies”